[논문리뷰] Style Transformer for Image Inversion and Editing (CVPR ‘22)
논문 스터디에서 진행하는 첫 논문 리뷰입니다. GAN inversion / editing task에 대한 지식도 부족하고 논문 리뷰도 처음이다보니 내용이 많이 어설픈 것 같네요. 다음 리뷰에서는 부족한 점을 보완해보겠습니다. (인라인 수식 에러는 새로고침을 통해 해결하실 수 있습니다.)
1. Introduction
StyleGAN을 활용한 Inverting과 Editing에는 어려움이 존재합니다.
Several candidate latent embeddings ($Z$, $W$, $W^+$)
여러 latent embeddings 중 noise ($Z$), latent code ($W$)와 비교하여 18 different latent codes ($W^+$)의 풍부한 표현력이 Inverting task에는 적합한 것으로 보입니다. 하지만 Editing task에서 $W^+$ space에 대한 충분한 regularization 없이는 잘 되지 않고 있습니다.
- (참고) Regularization은 e4e 논문에도 등장하는 개념인데, e4e 논문의 저자는 offset을 도입하여 single code를 multi codes로 점진적 확장함으로써 variation을 낮춘 multi codes를 얻어야 editability를 높일 수 있다고 했습니다.
distribution in $W$ or $W^+$ are complex
- Attribute가 latent space 상에서 entangled 되어 있을 경우 editing이 어렵게 됩니다.
이에 저자들은 encoder-based 접근 방식에 transformer block을 접목하여, inverting과 editing을 모두 잘할 수 있는 latent codes $W^+$를 찾고자 합니다.
또한, 지금까지는 binary attribute의 경우 latent space 상에서 선형 분리된다는 가정이 있었기 때문에 모든 이미지에 대해 same direction으로 editing을 했습니다. 하지만 저자들은 이러한 direction 결정 방식은 최적이 아니라고 주장하며, label-based editing과 reference-based editing을 통해 각 이미지에 대해 고유한 direction을 결정하는 방법을 제안합니다.
본 논문이 기여한 바를 요약하면 다음과 같습니다.
Multi-stage style transformer in $W^+$ space to invert image
Editing vector를 생성하는 비선형 classifier를 통한 label-based & reference-based editing
2. Related Works
GAN Inversion
Encoder-free
- 별도의 network 없이 latent code가 최적화되는 방식으로, 아직까지는 editing이 잘 되지는 않는다고 합니다.
Encoder-based
- CNN(encoder)에서 추출한 feature를 활용하여 latent code를 최적화하는 방식으로, IDInvert, pSp, ReStyle, e4e 등의 논문이 이에 해당됩니다.
Latent Code Manipulation
Unsupervised
GANSpace, Sefa 등 $W$ space에 대해 PCA를 활용하여 principal direction을 구하는 시도들이 있었지만, 이는 모든 이미지에 대해 same direction으로 editing한다는 단점이 존재합니다.
Pixel domain으로의 접근, contrastive loss의 적용을 통해 editing direction을 모델이 직접 찾게 하는 시도들도 있었습니다. 이는 각각의 이미지에 not same direction을 적용한다는 점에서 개선점이 있지만, unsupervised 방식의 한계로 인해 적은 수의 direction만 찾을 수 있었습니다.
Supervised
Label-based editing
Same direction
InterfaceGAN : latent space 상에서 선형 binary SVM classifier를 학습하여, attribute 조절이 가능한 normal vector를 가진 separation plane을 찾는 framework를 제안했습니다.
(보완 예정) StyleSpace : semantic mask를 활용하여 attribute 조절에 관여하는 channel을 찾는 방법과 함께, latent code W에 affine layer를 추가한 $S$ space를 제안했습니다.
(보완 예정) Not same direction
StyleFlow : Continuous Normalizeing Flows (CNF)
Latent transformation module
CNN encoder to provide multi-scale features to supplement the 1x1 style vector
Reference-based editing
- Editing in Style 논문에서는 각 channel에 담긴 정보를 구분할 수 있는 channel-wise mask에 k-means clustering을 적용하는 방법을 제안하였습니다.
3. Framework of Style Transformer
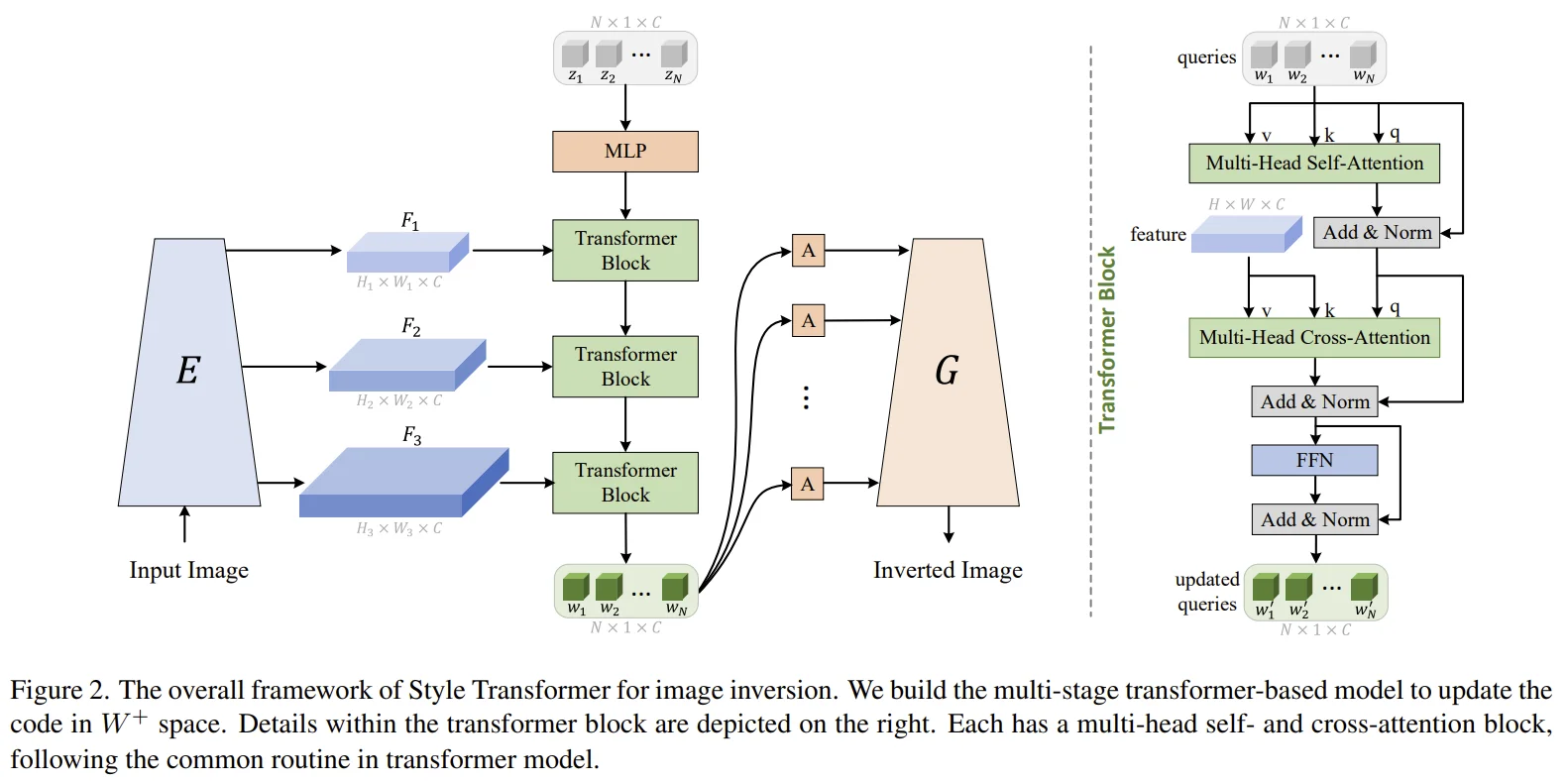
Style Transformer Block
Style query initialization
- StyleGAN의 pretraind MLP를 사용하여 noise vector z를 style query로 mapping합니다.
Multi-Head Self-Attention
- Style query에 대한 self-attention을 통해 query 사이의 관계를 학습합니다.
Multi-Head Cross-Attention
- Self-attention의 결과를 $Query$로, Encoder에서 추출한 image feature를 $Key$, $Value$로 하는 cross-attention을 통해 latent code와 image 사이의 관계를 학습합니다.
이후, FFN layer를 거치는 것으로 하나의 Transformer Block이 끝나게 됩니다.
Training Objectives for Image Inversion
학습 과정에서 StyleGAN의 Generator $G$와 affine layer $A$는 Freeze됩니다.
Losses
Notations
$I$ : input image
$\hat{I}$ : inverted image
L2 loss
- LPIPS loss ($F$ : Inception net)
- ID loss ($R$ : pretrained ArcFace model), (<> : cosine similarity)
4. Image Editing in Style Transformer
Fixed StyleGAN을 활용한 image editing은 그 자체로도 의미가 있지만, image inversion의 성능 측정에도 중요한 역할을 합니다. 성능에는 2가지 측면이 있습니다.
Low distortion : input image와 inverted image 사이의 일치도 (latent code로부터의 복원력)
Flexible and high fidelity editing : 유연하면서 일관적인 editing이 가능한가
Style code에 대한 editing을 수식으로 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
$w^s$ : source image에 대한 inverted style code
$w^e$ : source image에서 수정된 inverted style code
$\Delta w$ : editing offset
$\widetilde I$ : edited image
$G$ : styleGAN Generator
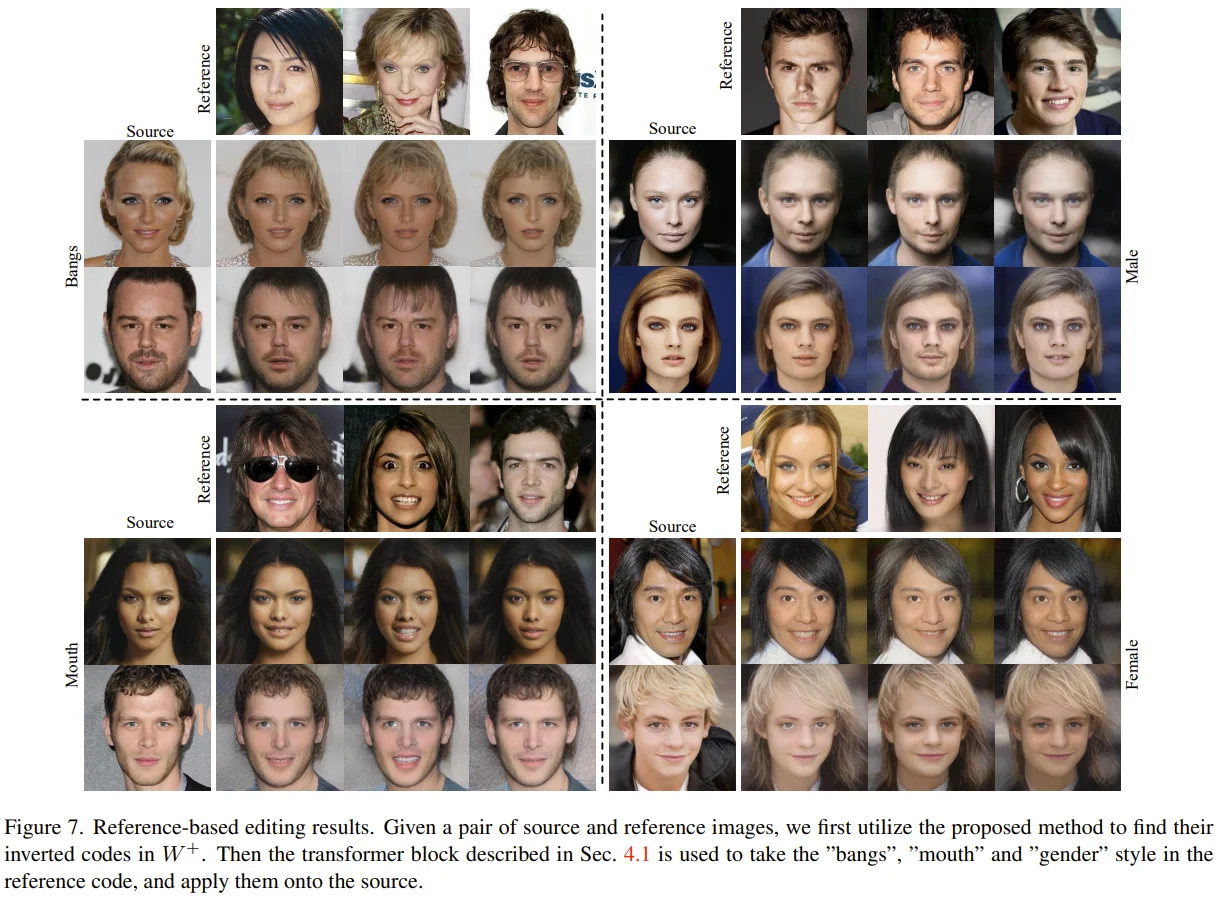
Reference-based Editing
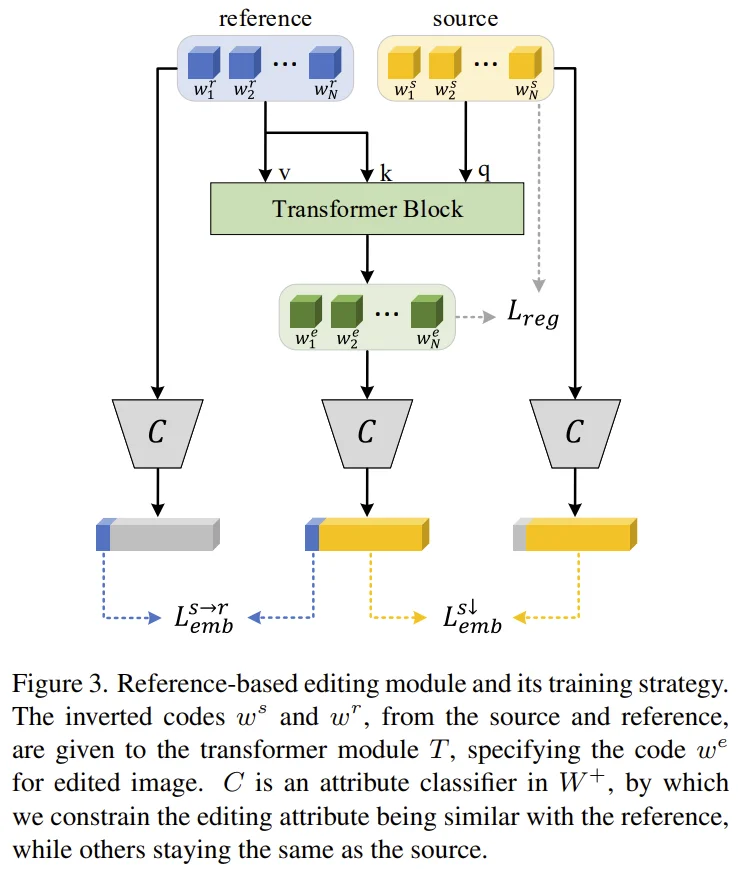
Module design \[T(w^s, w^r) = \Delta w = Norm_K (Softmax_Q (\frac {QK^T} {d^{1/2}}))V\]
$w^r$ : reference image에 대한 inverted style code
먼저, $w^s$에 대한 Self-attention을 수행합니다. 그 다음 self-attention의 결과를 $Query$로, $w^r$을 $Key$, $Value$로 cross-attention을 수행하여 $w^e$를 얻게 됩니다.
(보완 예정) 여기서 중요한 점은 $Softmax_Q$와 $Norm_K$를 통해 $w^r$의 value token이 $w^s$의 일부 token에만 영향을 준다고 합니다. (?)
Loss design
$C^k_f$ : $k$th attribute embedding features from latent classifier $C$
$\mathcal{L}^{s \rightarrow r}_{emb}$ : edited attribute는 reference image와 같아지도록 학습
- $\mathcal{L}^{s \downarrow}_{emb}$ : 대상이 아닌 attribute는 source image와 같아지도록 학습
- $\mathcal{L}_{reg}$ : edited image가 source image로부터 많이 다르지 않도록
Label-based Editing
Reference-based에 비해 간단하기 때문에, latent classifier $C$로 inverted latent codes를 수정하는 encoder-free method를 적용했습니다.
저자들은 모든 image는 $k$th attribute editing을 위한 고유한 direction $n^k_{\Delta w}$를 가진다고 주장합니다. 그리고 이는 classifier $C$의 backprop.을 통해 결정된다고 합니다. 수식은 다음과 같습니다. \[g = \nabla _w L_{bce} (C^k_l(w^s),y_t)\]
$g$ : the first-order gradient on $w$
$y_t$ : target label
$C^k_l(w^s)$ : the logits after sigmoid
- $n^k_{\Delta w}$ : unique direction for the $k$th attribute editing
$H$ : Hessian matrix
$d$ : randomly sampled unit vector
$\xi$ : small number
(보완 예정) Power iteration에 의해 $g = Hd$로 표현된다고 하며, 이를 통해 $n^k_{\Delta w}$가 존재함을 밝혔습니다.
- (참고) 선형대수학 내용으로 확인되는데, 자세한 내용은 모르겠습니다.
5. Experiments
- Pretrained StyleGAN2를 사용하였고, multi-scale feature 추출이 가능한 pSp encoder를 base로 하였습니다.
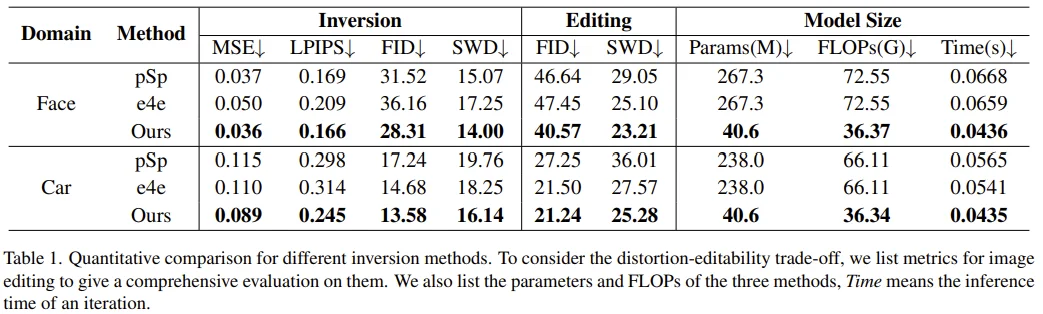
Inversion Results
Editing task의 경우, 성능 비교를 위해 InterFaceGAN (face), GANSpace (car)로 editing direction을 찾았다고 합니다.
Convnet과 비교할 때, 겨우 18 (face), 16 (car) token을 사용한 점에서 transformer 방식이 가볍고 효율적인 방법임을 알 수 있고, 이는 또한 성능에서 나타나고 있습니다.
Editing Results
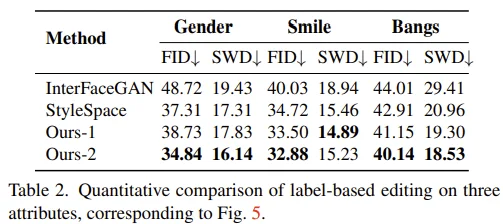
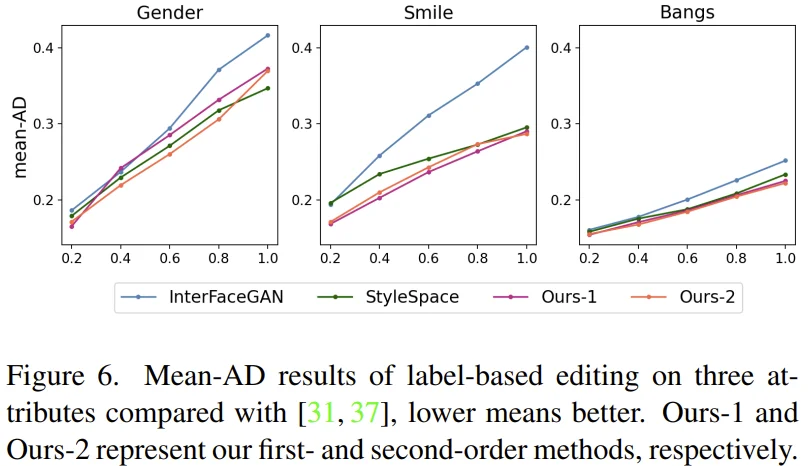
Label-based Editing
- InterFaceGAN, StyleSpace와 비교하여 좋은 성능을 보이고 있습니다.
Attribute Dependency (AD) : attributes 간 disentanglement 측정하는 지표입니다.
(보완 예정) Input image와 edited image 사이의 변화량을 normalize하여 AD score를 구할 수 있습니다. 여기서 $k$ attritbue에 대한 mean-AD를 구하기 위해서는 $not k$ attributes에 대한 AD의 평균으로 구할 수 있습니다. (?)
Reference-based Editing

6. Limitations
Inversion task
Input image와 reconstructed image 사이에 약간의 차이가 있는데, 특히 out-of-domain input에 취약하다고 합니다. 저자들은 $W+$ space의 finite discriminative에서 기인한 것으로 생각하고 있습니다. 이는 High-Fidelity GAN Inversion for Image Attribute Editing (CVPR ‘22) 논문에서 언급한 것처럼 source로부터 더 많은 정보를 가져오면 해결될 수 있다고 합니다.
Multi-head attention의 complex matrix multiplication
Reference-based editing task
- Latent space 상에서 학습이 이루어지다보니 image 자체를 수정하는 방식보다 diversity는 부족하지만, 모든 이미지에 적용 가능하며 가볍고 flexible하다는 장점이 있습니다.
7. Conclusion
중복되는 내용이긴 하지만 논문 이해에 도움이 될 것 같아서 원문 그대로 가져왔습니다.
This paper presents a transformer-based image inversion and editing method for StyleGAN. We choose W+ space to represent real images, which needs to determine multiple style codes for different layers of the generator. To effectively exploit information from input image, we design a multi-stage transformer module, which mainly consists of the self- and cross-attention. In the initial stage, the MLP maps a set of learnable noise vectors into the codes in W+, and then they are iteratively updated by the two types of attention operations, so the codes from the final stage can reconstruct the input accurately. Based on them, we are able to carry out label- and reference-based editing in a flexible way. Given a required label, an encoder-free strategy is employed to find the unique editing vector according to the gradient from a pretrained latent classifier. Meanwhile, given a reference code, a transformer block is trained to edit the source, so that the result takes the relevant style from the reference. Experiments show the proposed image inversion and editing method achieves less distortions and higher quality at the same time.