[논문리뷰] IPViT: Intriguing Properties of Vision Transformers (NIPS ‘21 Spotlight)
간단 요약
- ViT는 self-attention 덕분에 flexible receptive field를 갖기 때문에, CNN 계열의 feature보다 ViT의 feature가 robust하다.
- DeiT와 유사하게, shape token + shape distillation (from ResNet50-SIN feature)를 적용하여 ViT에 shape information 주입이 가능함을 보였고 (잘 된다기 보다는 가능하다의 느낌), 이를 통해 segmentation 성능 향상 및 shape bias 향상 효과가 있었지만, distribution shift에 취약해지는 모습도 보였다.
Abstract
ViT는 encoding된 image patch의 sequence 내에서 multi-head self-attention을 활용하여 flexible attention이 가능합니다. 저자들은 ViT가 natural image에 robust한 이유도 이러한 flexibility에서 기인한 것이라 생각하였고, 실험을 통해 다음의 특성들을 밝힙니다.
- Transformer는 occlusion, perturbation, domain shift에 robust하다.
- Occlusion에 robust한 이유는 texture bias에 집중하기 때문이 아니라, CNN에 비해 local texture에 less biased되어 있기 때문이다.
- ViT에 shape representation이 encoding 되도록 학습을 하면 (shape token 추가), pixel-level supervision 없이도 semantic segmentation 성능이 준수하다.
- Finetuning, few-shot learning을 한 이후, ViT의 여러 block에서 얻은 feature로 ensemble을 하면 더 높은 성능을 기대할 수 있다.
ViT feature가 이러한 특성들을 가질 수 있는 이유는 self-attention을 통해 flexible하고 dynamic한 receptive filed를 갖기 때문이라고 주장합니다.
1. Introduction
저자들은 robustness와 generalization의 관점에서 convolution과 self-attention을 비교합니다.
- Convolution : content-independent (input과 무관하게 same filter weight로 feature를 추출함)
- Self-attention : content-dependent (다른 embedding과의 interaction을 통해 global relationship을 고려할 수 있음)
즉, ViT는 receptive field를 flexible하게 조절함으로써 좋은 representation을 뽑아낼 수 있게 됩니다.
또한, DeiT 학습 구조와 비슷하게, shape token을 추가하여 shape-information을 encoding할 수 있는 training architecture를 제안합니다.
2. Related Work
대부분의 vision task에서 강점을 보이던 CNN은 i.i.d setting에서 좋은 성능을 보였지만 distribution shift에 민감하다는 문제점이 있습니다. 그런데 ViT는 distribution shift에 강건한 것으로 보입니다. 선행 연구에서는 ViT가 high frequency change, spatial perturbation에 robust함을 보였습니다. 본 논문에서는 image patch 측면에서의 robustness를 다루며, 이와 유사한 관점에서 접근한 Vision Transformers are Robust Learners 논문에 대해, 비슷한 주제지만 실험의 종류가 상이하다고 언급합니다.
또한, shape과 texture feature 사이의 mutual information에 대한 내용도 언급합니다. 본 논문에서는 ViT가 less texture bias를 갖기 때문에, shape information에 더 집중할 수 있다고 주장합니다.
마지막으로 CNN feature들을 시각화했던 선행 연구들과 유사하게, ViT feature를 시각화를 통해 ViT의 receptive field는 초기 layer에서 입력된 이미지 전체를 cover하며 layer가 깊어질수록 특정 영역에 집중함을 보입니다.
3. Intriguing Properties of Vision Transformers
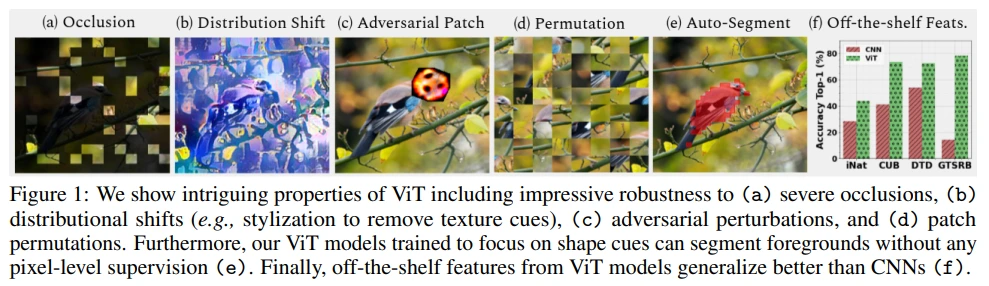
Figure 1을 통해 앞으로 어떤 실험을 할지 간단히 확인해볼 수 있습니다.
3.1. Are Vision Transformers Robust to Occlusions?

Occlusion을 구현하는 방법은 많겠지만, 본 논문에서는 간단히 masking strategy를 적용했습니다.
- Random PatchDrop : 이미지의 절반에 해당하는 patch를 radom drop
- Salient (foreground) PatchDrop : self-supervised DINO 모델의 feature 중에서 salient에 속할 가능성이 높은 feature drop (DINO는 salient object를 segment할 수 있음)
- Non-salient (background) PatchDrop : salient patchdrop과 유사한 방식을 반대로 적용 (salient에 속할 가능성이 낮은 feature drop)
Robust Performance of Transformers Against Occlusions
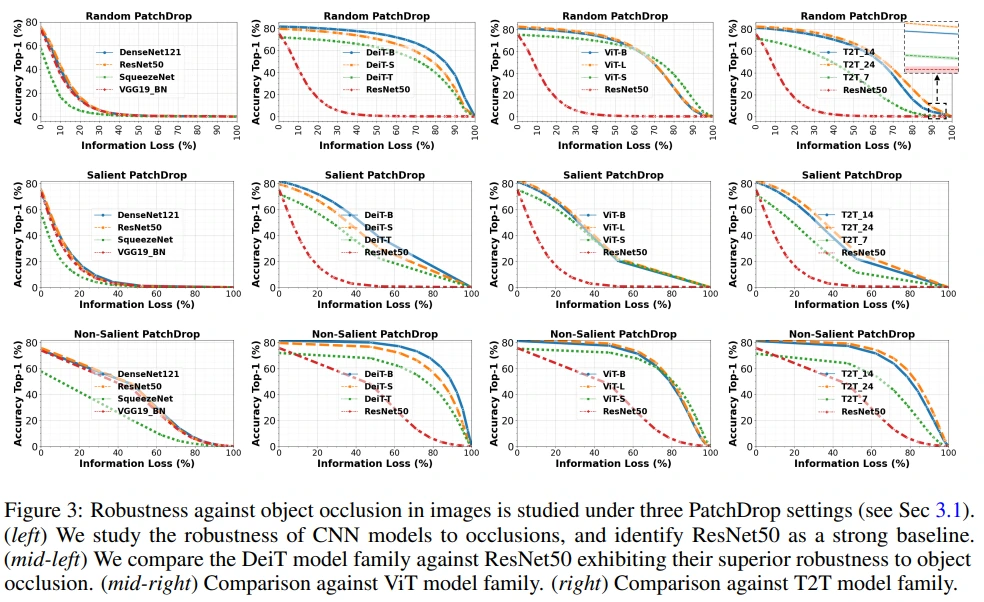
Figure 3의 가로축, Information Loss는 dropped patch의 비율입니다.
CNN(VGG19, ResNet50, SqueezeNet, DenseNet121) 계열의 모델 보다 ViT(DeiT, ViT, T2T) 계열의 모델이 PatchDrop(Occlusion)에 robust한 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
여담으로 MLP-Mixer에서 비슷한 실험을 본 기억이 있어서 찾아봤는데, IPViT 실험이 먼저인 것으로 보입니다.
- 2021.05.04 MLP-Mixer arXiv v1
- 2021.05.21 IPViT arXiv v1
- 2021.06.10 MLP-Mixer arXiv v3 : Section 3.4 Invariance to input permutations 추가 (Figure 4)
Appendix의 다양한 실험에서도 위 결론을 뒷받침하는 실험 결과가 나왔습니다.
- Appendix A : masking grid size 변경
- Appendix B : pixel drop
- Appendix C : feature drop
- Appendix D : RegNetY, Swin transformer 추가
- Appendix E : SIN dataset으로 학습된 모델 간 patch drop 및 patch shuffle 성능 비교 (patch shuffle에서는 ResNet50-SIN이 DeiT-S-SIN 보다 좋은 성능)
ViT Representations are Robust against Information Loss
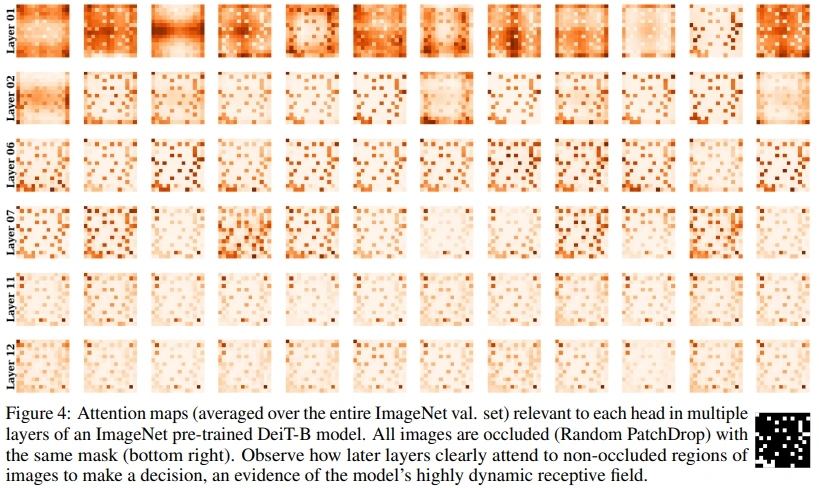

Figure 4에서 우측 하단의 black-white map이 PatchDrop에 사용된 mask입니다.
초기 layer에서는 이미지 전체에 attention되어 있는데, layer가 깊어질수록 masking되어 있지 않은 pixel에 집중하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
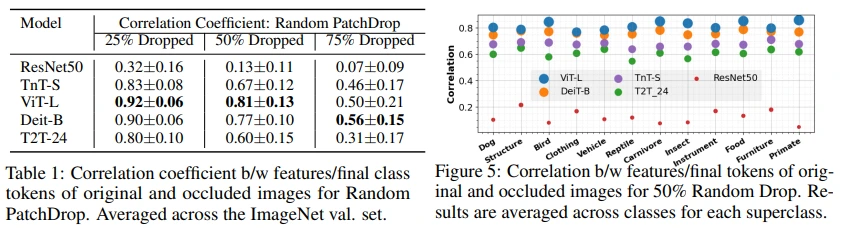
저자들은 이를 수치로 나타내기 위해, CNN의 feature, ViT의 class token에 대한 original/occluded image의 correlation coefficient로 measure하였습니다.
즉, original 이미지와 PatchDrop(=occluded) 이미지에서 얻는 feature의 유사성을 나타내는 값으로, ResNet50보다 ViT에서 유사한 feature를 추출하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. (=robust)
3.2 Shape vs. Texture: Can Transformer Model Both Characteristics?
background : Imagenet-trained cnns are biased towards texture
SIN : stylized version of ImageNet
솔루션 : SIN, IN으로 pretrain한 다음, IN으로 fine-tune하면, texture bias를 줄이면서 shape bias를 높일 수 있다.
위 방식으로 학습한 모델 : ResNet50-SIN
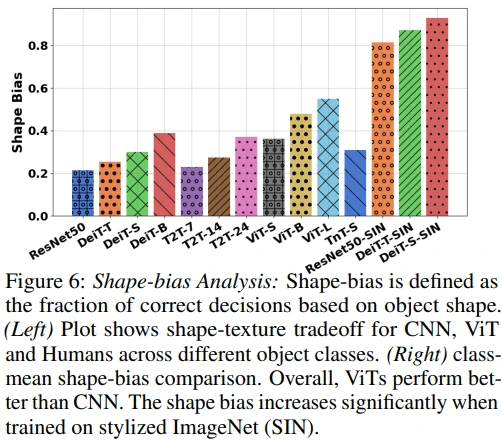
먼저, Imagenet-trained cnns are biased towards texture 논문에서 제안한 shape-bias analysis를 수행합니다. Figure 6를 보면 ViT가 CNN에 비해 shape-bias가 더 강하지만, 그럼에도 texture에 더 집중하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Training without Local Texture
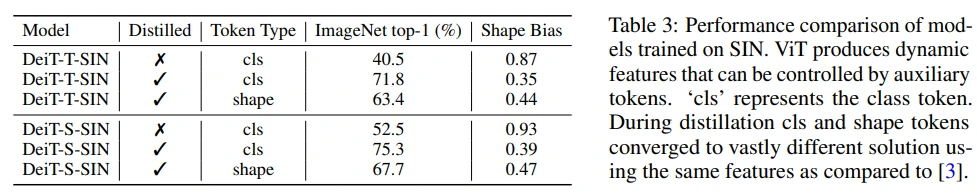
ViT의 shape-bias를 높이기 위한 목적으로 background 논문의 솔루션을 적용하여 SIN dataset을 학습한 결과 shape-bias는 강해졌지만, DeiT-T-SIN(40.5), DeiT-S-SIN(52.5)로 accuracy가 매우 많이 떨어지게 됩니다. (Table 3 각 모델의 첫 줄 참고)
Shape Distillation
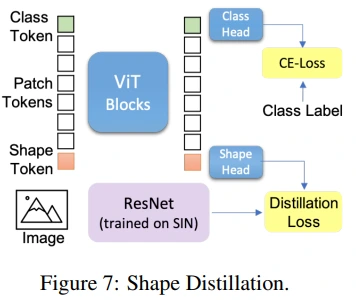
이에, 저자들은 DeiT를 참고하여 shape token을 추가하고, ResNet50-SIN 모델로부터 shape information이 distillation되는 training framework를 제안합니다. (Figure 7)
Table 3에서 distillation하지 않았을 때와 비교하여 accuracy가 많이 상승하였고, shape token을 통해 accuracy는 약 10% 희생되지만 shape bias가 향상되는 것도 확인할 수 있습니다. (token type이 cls인 경우는 distillation을 어떻게 한건지 잘 모르겠네요. DeiT와 비슷하게 했으려나 추측됩니다.)
Shape-biased ViT Offers Automated Object Segmentation
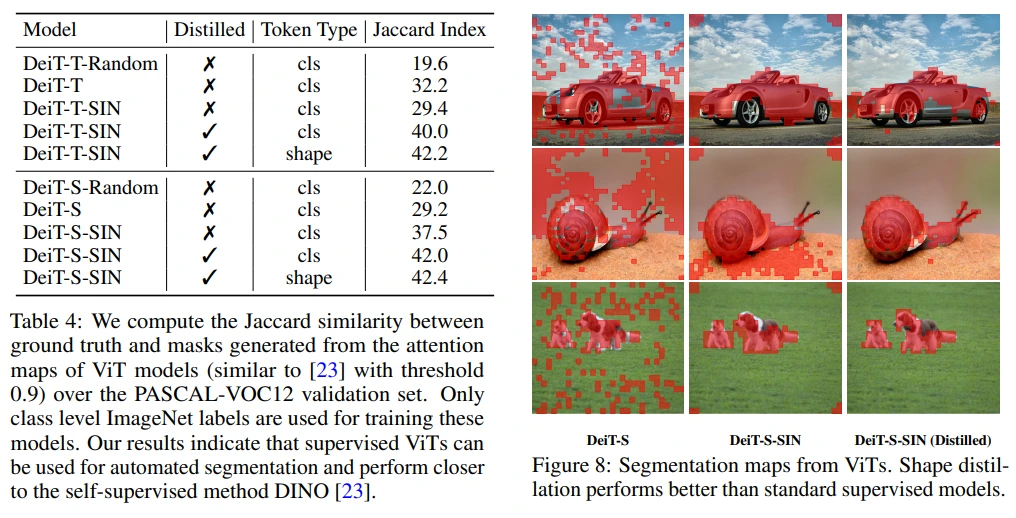
Table 4와 Figure 8에서 SIN + shape token + shape distillation의 효과를 확인할 수 있습니다.
3.3 Does Positional Encoding Preserve the Global Image Context?

이미지의 structural information 제거 목적으로, grid 내에서 random shuffle이 적용된 결과입니다.
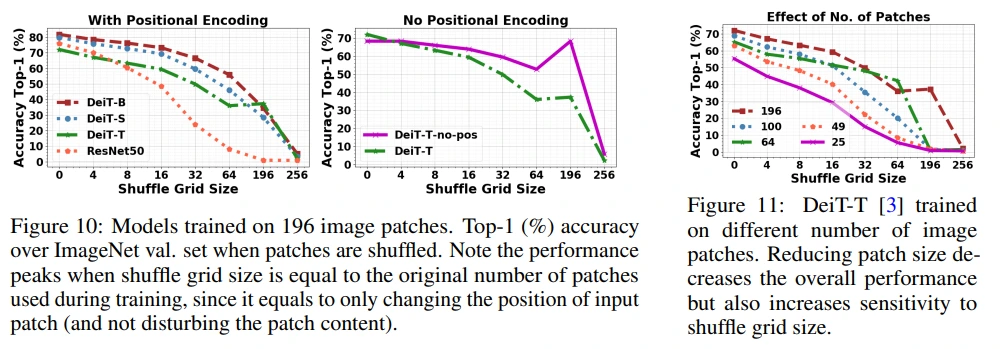
Figure 10을 통해 ViT가 occlusion에 robust한 이유가 positional encoding에서 비롯된 것이 아님을 보입니다.
Figure 11에서는 ViT의 permutation invariance 특성을 확인할 수 있습니다. (물론 suffle grid size 값이 커짐에 따라 accuracy가 점점 0에 도달하긴 하지만, CNN보다는 robust할 것이 예상됩니다.)
3.4 Robustness of Vision Transformers to Adversarial and Natural Perturbations
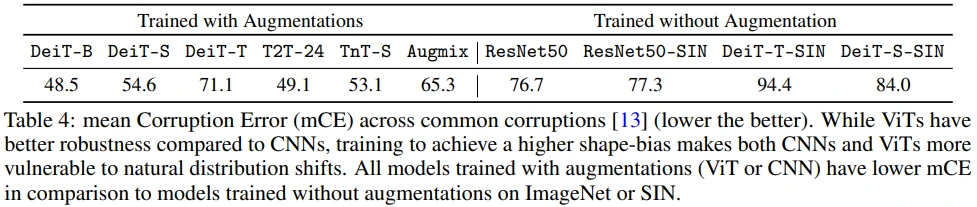
Common corruption(ex. rain, fog, snow, noise)에 대한 mean cooruption error (mCE)를 측정합니다.
- 전체적으로 augmentation을 통해 corruption에 robust해지는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 좌측의 augmentation 결과만 보면 Augmix(ResNet50)보다 ViT 계열의 mCE가 더 낮지만,
- 우측의 without augmentation 결과에서는 CNN 계열이 더 낮은 mCE를 갖는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. (이에 대해 저자들은 shape bias가 주입되면서 natural distribution shift에 취약해졌다고 주장합니다.)
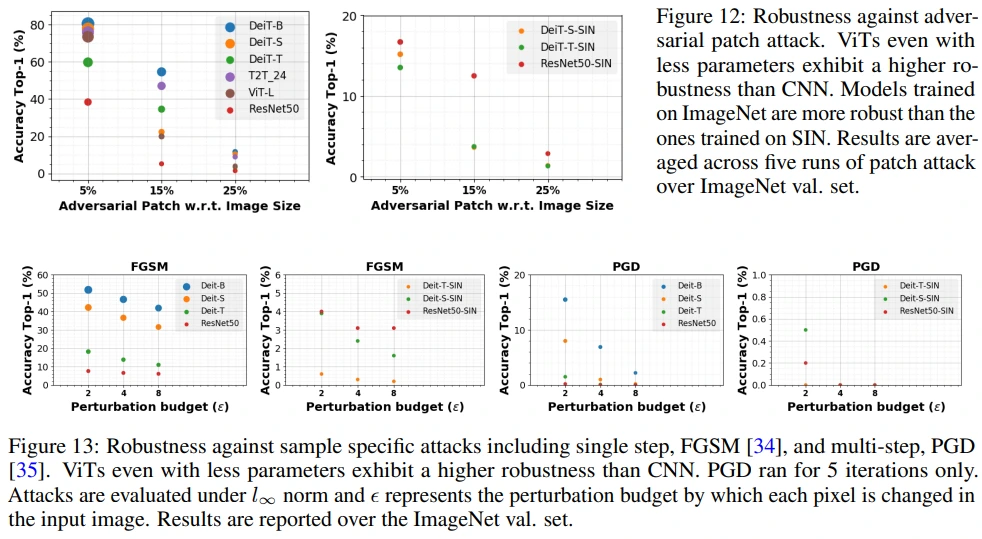
앞에서의 결론과 비슷합니다.
CNN에 비해 ViT가 adversarial patch attack, perturbation 등에 대해 robust하지만, shape bias가 주입된 ViT-SIN보다는 CNN-SIN이 더 robust함을 확인할 수 있습니다.
3.5 Effective Off-the-shelf Tokens for Vision Transformer
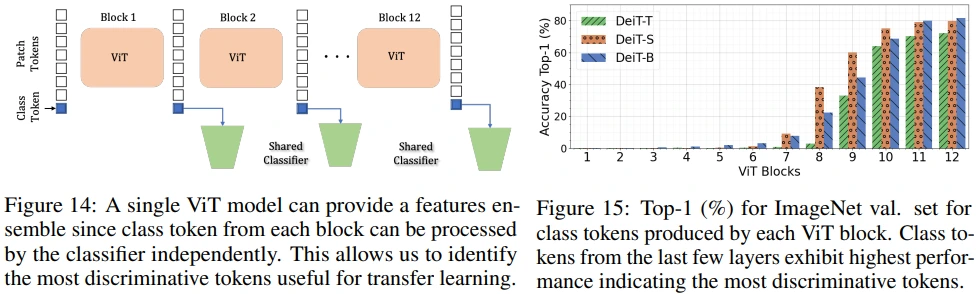
각 ViT block의 class token별로 accuracy를 측정하였는데, layer가 깊어질수록 더 좋은 성능을 보이고 있습니다.
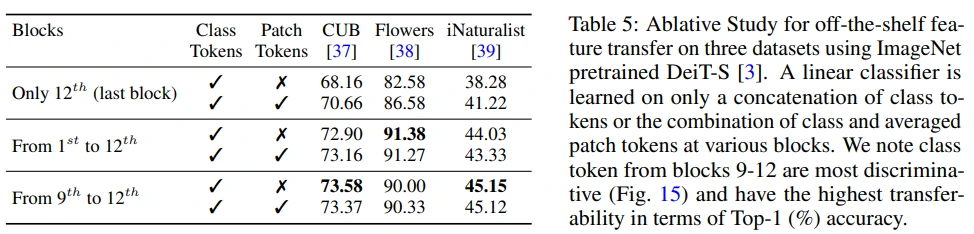
그리고 어떤 block에서 token을 가져올지, patch token을 추가로 사용할지 등의 실험을 했습니다. (class token은 concat하였고, patch token은 average를 해주었습니다.)
Last block만 사용하는 것보다 여러 block의 token을 사용하는 것이 성능은 좋았지만, 이처럼 token을 많이 사용할수록 trade-off로 시간이 오래 걸리게 됩니다. (본 논문에서 feature ensemble이라고 명명한, ViT의 여러 layer token을 함께 사용하는 경우는 self-supervised DINO에서도 확인할 수 있습니다.)
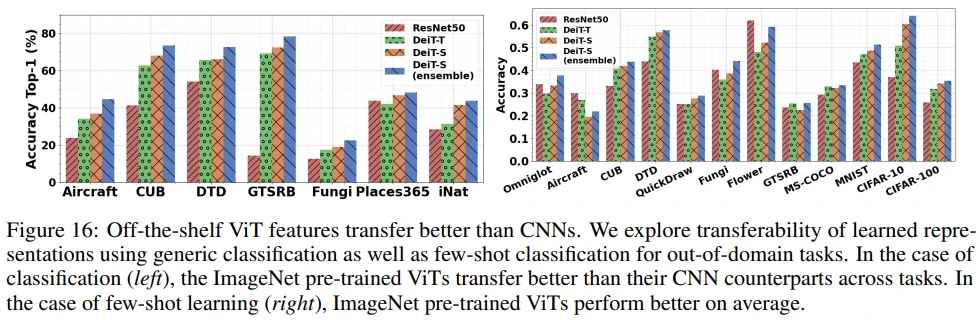
좌측의 fine-tuning, 우측의 few-shot learning setting에서 대체로 ResNet50 feature에 비해 DeiT feature의 fine-tune 성능이 좋았고, feature ensemble도 효과가 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Future work
- SIN Dataset에 대한 self-supervision이 DINO의 segmentation 향상에 기여할 수 있을지 ?
- Self-supervised DINO를 학습시킬 때 texture based local view, shape based global view 관점을 추가하면 어떨까 ?